Schaeffler India actively takes calculated business risks to achieve its corporate objectives and implement its strategy. We have a comprehensive Risk Management System (RMS) that ensures timely risk identification, evaluation and analysis of mitigation plans, as well as the identification of improvement areas to minimise any negative impact on our operations.
Our risk categories encompass strategic, operational, legal, financial and ESG-related risks, which are integrated into our catalog. Risks are reviewed every six months, with significant updates made regularly. Additionally, opportunities are considered in our risk identification process.
The Risk Management System (RMS) is overseen by the Board of Directors and is supported by the Risk Management Committee (RMC), which is constituted according to the provisions of the Companies Act. The details of the RMS are outlined in a risk management guideline that is accessible to employees responsible for risk management and is mandatory for them to follow. This guideline includes a description of the risk management process, allocation of responsibilities, and the structure for risk assessment and reporting.
Under the guidance of the RMC, the Risk Management Working Group (RMWG) operates as a bridge between various functions and divisions of Schaeffler India and the RMC of Schaeffler India’s Board. The RMWG monitors, reviews, and facilitates the effective implementation of risk management at Schaeffler India while also providing valuable feedback to the RMC.
Risk assessment is conducted in a hierarchical format using a bottom-up approach. The process owner for each risk area evaluates the risk, assesses its potential impact on the Company’s earnings and assets, and reviews the risks in relation to the budget. The process owner also outlines the existing mitigation plans aimed at offsetting any adverse effects. If these plans are deemed insufficient, additional measures are identified for implementation. The RMWG analyses the risk assessments and offers input to further protect the Company’s assets.
A value-added report is created by the RMWG and presented to the RMC for review. The RMC then provides a report to the Board of Directors, ensuring that they are kept updated on the current risk situation of the Company.
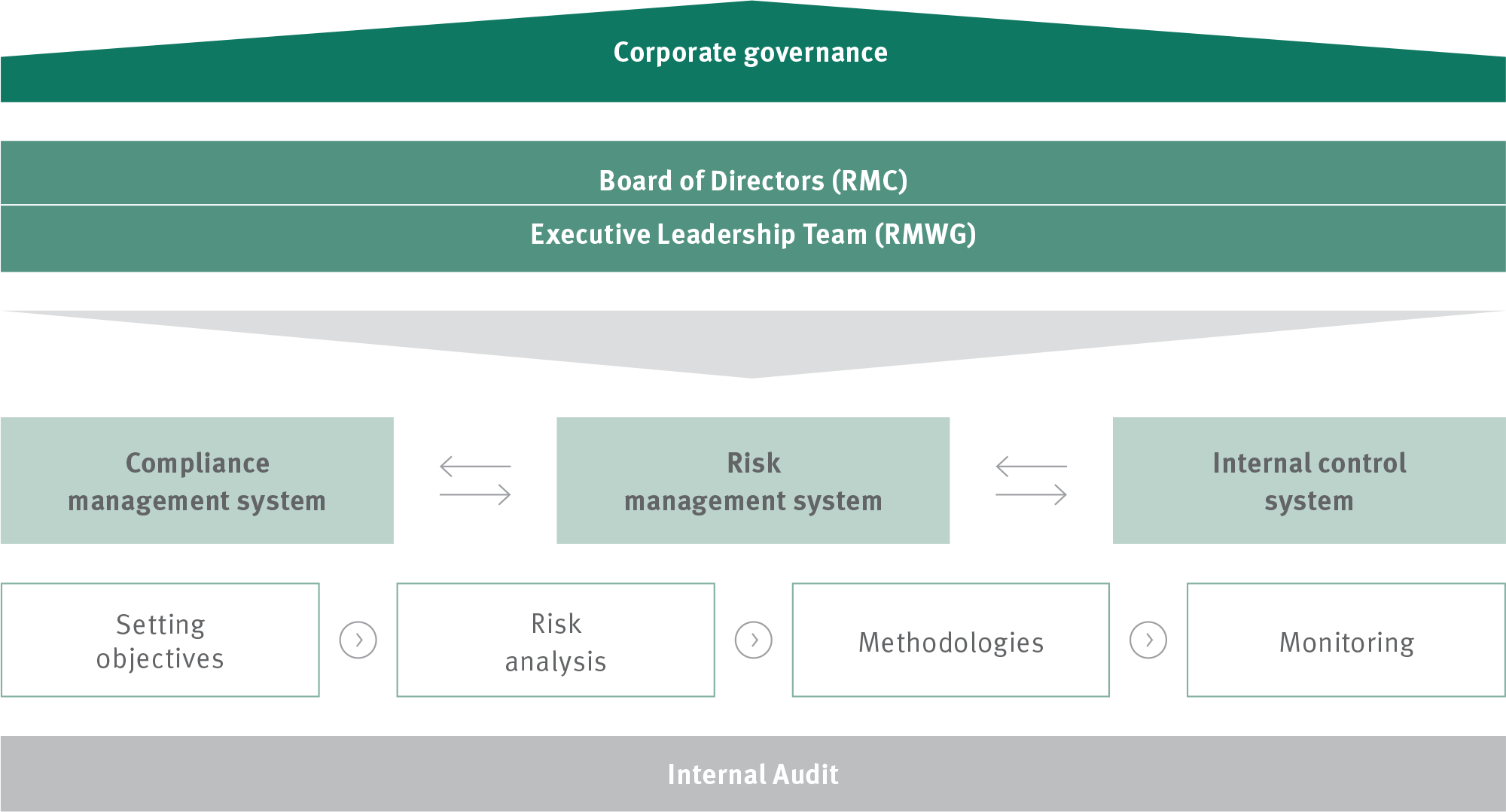
The Risk Management System (RMS) also takes place in conjunction with the Internal Control System and Compliance Management Systems. Risks are identified and managed in their environment. The controlling function, in which the planning and forecasting process risks are reflected, plays an important role.
The Board of Directors of Schaeffler India has established and approved the company’s risk management strategy. Schaeffler India takes calculated business risks in a prudent manner to achieve its strategic objectives and capitalise on related opportunities. Generally, business success depends on the ability to seize opportunities while also recognizing, assessing, and managing risks at an early stage.
Schaeffler India’s risk strategy provides a framework for determining which risks should be avoided and which can be maximally accepted. According to this strategy, each employee is responsible for entering into and managing business risks responsibly within their assigned area.
Additionally, it is essential to identify risks that could jeopardise Schaeffler India’s ongoing viability at an early stage. The early warning system, part of the risk management framework, aims to promptly communicate identified risks and their impact on the Company’s net assets and financial position. Consequently, the early warning system is reflected in ad hoc reporting, which requires that identified risks be reported immediately by the risk owner.
The objective of the risk management policy is to define the key goals of risk management, serving as the foundation for an effective and appropriate risk management system for Schaeffler India. In addition, the key objectives highlighted are as follows:

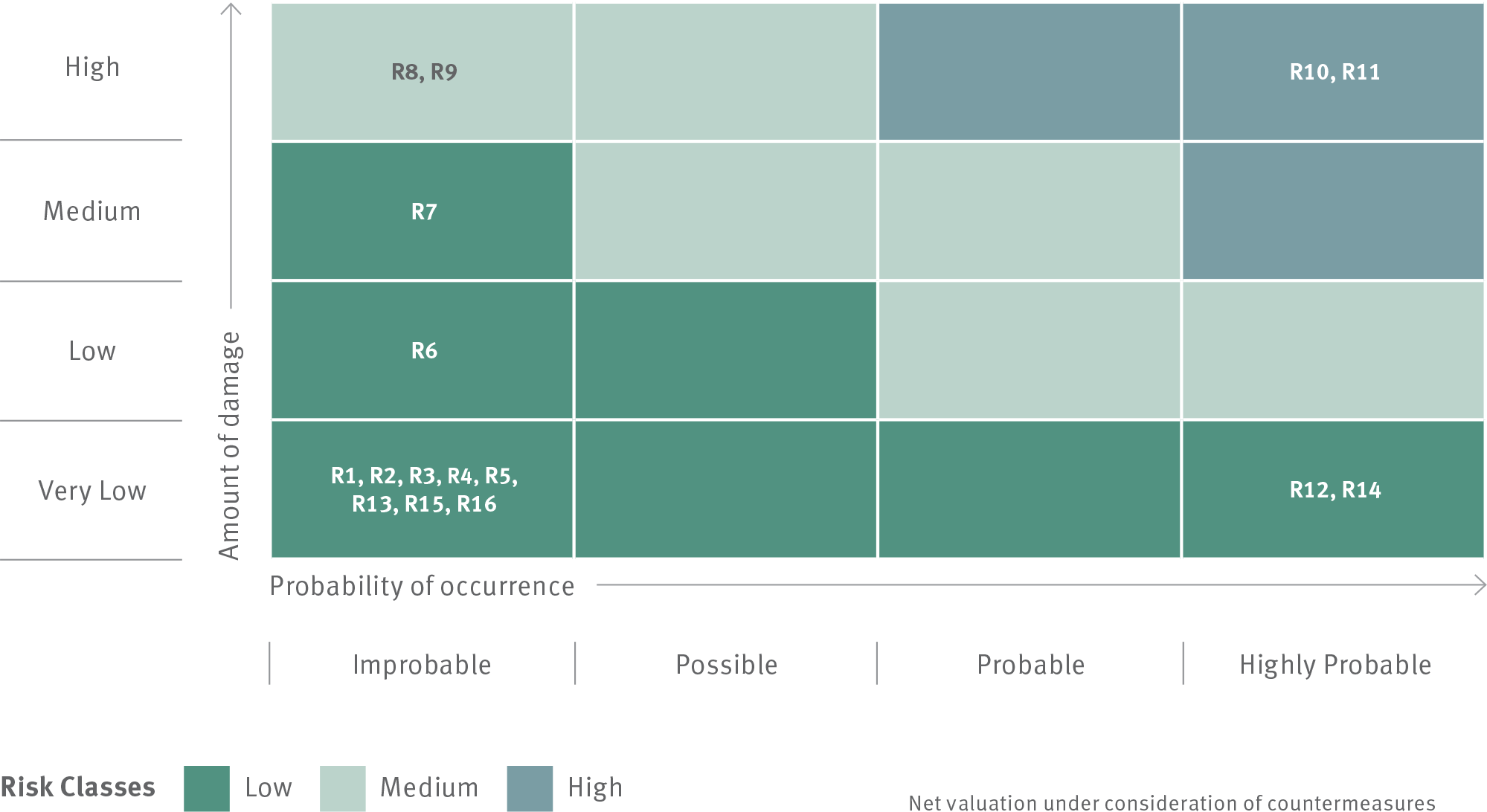
Risk assessment employs a two-dimensional approach that evaluates potential annual damage and the likelihood of occurrence. Risks are classified as very low, low, medium, or high based on damage, while probability is categorised as improbable, possible, probable, or highly probable.
The combination of damage and probability determines an overall risk class—very low, low, medium, or high— impacting net assets, financial position, and earnings. Each risk is assessed in two stages: before and after implementing mitigation measures, referred to as gross and net valuation. Risks are then assigned to classes based on net valuation using a risk matrix.

Amount of damage
Probability of damage
Risk Class
Basis of risk assessment
Risks are divided into strategic, operating, legal and financial risks and are described in decreasing order of the magnitude of their impact on the next assets, financial position and earnings of the company.
The key operational risks of the Company are listed below.
| Key risks | Mitigation measures |
|
R1. Production
|
|
| The Company’s capital-intensive manufacturing facility has a high proportion of fixed costs. As a result, reduced plant capacity utilization leads to under-absorption of costs, adversely affecting earnings. Additionally, force majeure events can cause production and supply chain delays, hindering the ability to meet market demand. Any delay in finding an alternative source after a plant failure could negatively impact the Company’s net assets and financial position. | The Company regularly reviews market conditions and adjusts its production plan accordingly. If needed, alternative sources can be utilised from other plants within the Schaeffler Group. To reduce the likelihood of unplanned interruptions, the Company implements extensive fire prevention measures. Additionally, several cost containment strategies have been identified and applied to address material and process costs. |
|
R2. Information Technology (IT)
|
|
| The importance of the IT systems utilised across various functions in the Company is growing. The operability of business processes and, therefore, the continuity of operations depend on the availability of IT systems. Three protection targets – confidentiality, integrity, and availability – steer the Company’s IT security management and protection of data and IT systems. Unauthorised access to IT systems, modification and misappropriation of sensitive business data could have an impact on the Company’s net assets, financial position and earnings. | The Company maintains the highest standards for its IT security systems and continually upgrades its IT security infrastructure. It provides education and training for employees on IT security best practices and the necessary precautions to protect the IT infrastructure and business data from potential risks. The Company also implements redundancy in its IT systems, including data backups on virtual servers and fire- and waterproof cabinets, as well as in its network infrastructure through secondary network lines. These measures help mitigate the risk of data and process unavailability. |
|
R3. Human resource
|
|
|
Staff shortage Scarcity/less availability of specific talent with right cultural fit. Also, critical talent retention can be a challenge in the backdrop of Talent War impacting the organization in the exploited market scenario. |
Retention and engagement measures are crucial for reducing risk. We are implementing an effective recruiting model designed to attract talent, accelerate the hiring process, enhance employee experience, and improve the quality of responses. We are also reviewing our compensation and reward policies through transparent, market-driven approaches. Additionally, upskilling and diversity and inclusion programmes will help us build a high-quality workforce. |
|
R4. Product piracy
|
|
| Counterfeiting will adversely affect our brand image and lead to reduction in projected sales volume. Most of the products selling by counterfeiters are regular standard products with trademark violation. Market investigations are in process to identify the counterfeiters and follow up action. Schaeffler India’s product brands (LuK, INA and FAG) are very popular and associated with high standards of quality, durability and reliability. This makes the brands increasingly susceptible to product piracy. | We protect our intellectual property. We continue to engrave special markings on our products, making it difficult to counterfeit. Our Company follows a strict vigilance process to ensure timely detection of counterfeiting instances and initiation of legal actions against the guilty. This is done in association with law enforcement agencies. Moreover, digital anti-counterfeit app is regularly upgraded to support these initiatives. We evaluate other technology-driven initiatives on an ongoing basis to overcome this risk. We also conduct awareness and engagement activities with our distributors. |
|
R5. Climate change related
|
|
| Extreme weather and climate change significantly impact businesses by damaging buildings and infrastructure, disrupting production and logistics, and affecting energy supply. These conditions can lead to the loss of suppliers, changes in the availability and quality of raw materials, and diminished employee performance. Business interruptions and damage to assets, including inventories, can result from flooding, storms, drought, and other severe weather events. | A technical assessment of the location was conducted using SwissRe’s ‘Risk Data & Services’ (RDS) database, evaluating the severity and likelihood of potential risks. To mitigate these risks, measures such as installing lightning arrestors, increasing water tank capacity, rainwater harvesting, designing drainage systems and conducting building stability checks have been implemented. Additionally, some processes have been relocated to lower-risk areas, along with the establishment of emergency and contingency strategies. |
|
R6. Procurement
|
|
| Procurement risks arise mainly due to raw materials price fluctuations, especially prices of energy and steel, ability of suppliers to deliver quality products in time. Adverse fluctuations in market prices and/or supplier’s financial distress could have an impact on the Company’s financial position and earnings. There is constant threat emanating from global supply chain disruptions and import restrictions due to EXIM policy amendments. | The Company ensures an optimal supply of goods and services, focusing on quality, cost and delivery performance. Multiple product sourcing and localisation options are continuously explored. By negotiating prices and utilising economic synergies, the Company is largely able to obtain competitive prices. The Company keeps a close watch on supplier operations by deploying dedicated personnel to perform quality checks for early signs of distress and be able to intervene to secure its interests. Forward buying option is undertaken in selected cases. |
|
R7. Delivery performance
|
|
| Consistently delivering high-quality products on time is essential for building trust with customers. Ongoing improvements in production and delivery logistics enhance this competitive edge. However, factors that affect delivery performance can lead to lost sales and higher logistics costs. Frequent delays may drive customers to competitors, resulting in a loss of market share. | The Company has high-performance distribution centres to improve market supply and delivery performance, with strategic logistics locations. Components sourcing options and capacity of critical production lines are also being enhanced. The accuracy of forecasting market demands, alternate sourcing and localisation are few measures that ensure timely delivery performance. |
|
R8. Fire
|
|
| Fire risk assessment is done to identify potential fire hazards in a workplace and evaluates the risk they pose. The goal is to prevent fires from starting and to ensure that people can safely evacuate if one occurs. Production stoppage most likely due to fire. But the probability of fire is very remote as establishment of effective safety management monitoring on daily basis. | To assess fire risk, particularly at plants and warehouses, we use the KPI Fire Protection tool. The tool has five evaluation criteria, viz. structural fire protection, organizational fire protection, technical fire protection, defensive fire protection, and fire protection officer. Evaluation and assessment of these KPIs are carried out at regular intervals. Additionally, we have other regular measures in place, such as all facilities being well-equipped with firefighting equipment, fire detection devices, etc. We have a Crisis Management team with on-site emergency plans in place. All our facilities regularly undergo safety audits by external and internal agencies. |
|
R9. Compliance
|
|
| As a Company with operations at different locations, it must comply with laws and regulations across the country. It is possible that violations of any existing law occur, despite careful observance of such legal requirements. | The Company has in place a comprehensive Compliance Management System, wherein laws and regulations applicable to the Company are mapped. Each compliance requirement is mapped to relevant process owner. The system sends alerts and reminders to each such process owner to enable him to comply with the requirements in a timely manner. Your Company’s management regularly reviews a comprehensive compliance report. The system is also updated regularly to capture regulatory changes and amendments. |
|
R10. Loss of market share
|
|
| We face competition in every field of our operations. As a result, we are exposed to dual risk of either being displaced by existing or new competitors or its products being replaced by product innovations or new technological features. Customer dissatisfaction on price, quality, delivery performance and design could lead to loss of market share. Risk of sales loss due to market driven factors leading to reduction in overall production demand. | We ensure close cooperation with our key customers on product development. It has implemented strict product quality controls to reduce the likelihood of substitution. We are developing products, which will help us to step up the value chain from components to systems. Some of the measures include efficient contract management, identifying new opportunities and expanding our local footprint to comply with local content requirements under the ‘Make in India’ programme of the Indian government. |
|
R11. Market developments
|
|
| As the Company is a supplier in the automotive and industrial sectors, demand for the Company’s products is, to a large extent, driven by macro-economic conditions and related cyclical fluctuation. Besides these, in the Automotive OEM division, demand is also affected by changes in consumption patterns, fuel/commodity prices, availability of key components, interest rate levels and so on. Cumulatively, these factors lead to significant volatility in automobile production. Sales in Industrial division is spread across diversified business fields and risk in one sector can be offset by opportunity in another sectors. A change in forecasted market trends could have an impact on the net assets, financial position and the earnings of both Automotive and Industrial markets. | Markets are analysed on an ongoing basis to detect changes in market structure or regulations early on. The Company effectively manages financial performance through cost efficiency, operational efficiency and price excellence programmes. New business opportunities are continuously sought after to overcome current market dynamics. |
|
R12. Warranty and liability
|
|
| One of the significant factor in customer decision to purchase the products offered by the Schaeffler is quality. We employ a certified quality management system besides continuously striving to improve quality processes. However, there is a risk that poor quality products get delivered. Usage of defective parts can lead to damages, unplanned repairs or recall on the part of customer which can result in liability claim or reputational damage. Furthermore, this may result in increase in warranty & liability risk. | The Company responds to such risks by adopting strict quality control measures and continually improving its production processes to minimise the probability of warranty and liability risks materialising. Adherence to quality standards is strictly implemented. All product and recall liability risks are insured. |
|
R13. Information or cybersecurity
|
|
| The ongoing threat of cyber attacks is a significant concern for organizations in today’s digital landscape. Cybersecurity remains a crucial focus for the company, and we invest substantial resources to safeguard our computer systems, software, and networks. However, despite these efforts, cyber attacks can still threaten our intellectual property and that of our business partners. With the increasing frequency and sophistication of these attacks, we cannot entirely eliminate the risk, which could impact the Company’s assets, financial position and earnings. | Cybersecurity initiatives have been implemented to mitigate potential incremental security threats from possible security risk exposures. The Company has reinforced and scaled up the internal environment to ensure the network is secured and healthy. Procedures and other IT security specifications supplement the information security regulations of the Company. Several technical measures have been established for any illegal intrusions and to mitigate the risk of cyber-attacks and secure data thefts which also includes monitoring the networks for cyber threats through the Security Operations Centre (SOC) to detect and respond to cybersecurity events. We will continuously buttress our cybersecurity defences and place responsible guidelines along with security controls to strengthen our security roadmap in managing risks in data, IT systems and cybersecurity across the Group businesses. |
The key financial risks of the Company are listed below:
| Key risks | Mitigation measures |
|
R14. Tax
|
|
| Your Company is subject to tax audits. Tax authority’s interpretation of the tax law or of relevant facts made in current or future tax audits may differ from that of the Company. This may lead to adjustments to tax base and increase in the tax liabilities. An additional tax payment because of an adjustment to the tax base may impact on the Company’s financial position. | The Company extensively evaluates Corporate Tax & International Tax laws, both internally and with external tax experts, before implementing those in the Company. The implementation strategy is well documented, reviewed periodically and amended as necessary. |
|
R15. Currency
|
|
| The Company is exposed to currency risks due to its cross-border transactions. The largest currency risks from operations result from fluctuations in the USD and Euro exchange rates. | Your Company has INR as the inter-company invoicing currency with German entities. This leads to a substantial reduction in its foreign exchange exposure and nullifies currency volatility impact. Additionally, the Company has a structured hedging strategy to counter currency risks. The strategy is followed consistently and reviewed periodically. The Company monitors overall FX development closely and revisit its FX strategy on a periodic basis. Sensitivity analysis is one of the measures used to mitigate risk. |
|
R16. Pension
|
|
| Your Company has pension obligations towards its employees. Such obligations are measured using actuarial valuation based on assumptions with respect to the discount rate, increases in personnel payments and statistical life expectancy. Planned assets are invested with external agencies, which are subject to fluctuations in value. A change in these parameters could have an impact on the Company’s net assets. | The Company uses the government bond rate as a discount rate and invests in a pension fund with a Government of India enterprise (LIC). Quarterly actuarial valuation is carried out, adequate provisions are established in books of accounts and annually funds are appropriately transferred to LIC. |